Some tasks do not require a graphical feedback. This kind of work can be managed with Android using:
- a service if it is a long running task (we can use a foreground service that is not killed by the system)
- a work submitted to the WorkManager API for a short running task that must be executed periodically (e.g. synchronization task)
Service
Principles
- A Service is an Android component that must be declared in the manifest.
-
It can be used to expose methods that can be synchronously called by the same or another application (it is not the preferred wey to manage tasks)
- If we do not expose remote methods, we must override IBinder onBind() to return null
- Or we can submit intents to the service to execute tasks
- The service is automatically started when a first intent arrives
- Intent must include explicitely the name of the class of the service (no implicit intents are authorized to start a service)
- Additional intents can be sent to a service when it is already started
-
The received intent is managed by the onStartCommand method of the service (that must be overriden)
- Like all the event methods, it is executed on the main thread of the application; the execution must be quick
-
For long-running tasks, a secondary thread must be used to not block the main thread
- Using Java, it can be managed with an AsyncTask
- Using Kotlin, a coroutine can be started using a secondary thread context : withContext(Dispatchers.Default)
-
A service has a limited graphical feedback
- With notifications (that can b used to launch activities)
- With toasts
A simple service displaying a toast
This simple example presents the use of a service: it displays a toast when it receives an intent.
Usually when we create a Service, we define actions (string constants) that are used in the intent to express the order given to the service. The action is set to the intent with setAction(String action).
We write the service:
public class ToastService extends Service {
/** An action that has an unique name */
public static final String TOAST_ACTION = ToastService.class.getName() + ".displayToast";
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
if (intent.getAction().equals(TOAST_ACTION)) {
String id = intent.getStringExtra("id");
String message = intent.getStringExtra("message");
boolean longDuration = intent.getBooleanExtra("longDuration", false);
Toast t = Toast.makeText(this, message, longDuration ? Toast.LENGTH_LONG : Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
t.show();
}
return START_NOT_STICKY; // if the service is killed, the intent will not be redelivered
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not implemented (since we do not use RPC methods)");
}
}
We write an activity that starts the service:
/** An activity submitting messages to a service displaying them as toasts */
class ToastServiceActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_toast_service)
sendButton.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent(this, ToastService::class.java)
intent.action = ToastService.TOAST_ACTION
intent.putExtra("message", messageView.text.toString())
intent.putExtra("longDuration", longDurationView.isChecked)
startService(intent)
}
}
}
Stopping and restarting the service
-
The service can be stopped:
- it will be automatically killed by the system when it is not used for a given time
- it can be stopped by hand using stopService(Intent intent) from an external component (e.g. activity) or the service can stop itself with stopSelf()
- The service will be restarted when a new intent arrives
- Before being killed, the onDestroy method of the service is executed (it can be overriden to release resources)
The int returned by the onStartCommand specifies what behaviour must be used when the service is killed by the system:
- The constant START_STICKY indicates that the service must be automatically restarted after being destroyed by the system; when restarted the onStartCommand is called by the system with a null intent; this behaviour is useful for long running tasks (like a music player)
- The constant START_REDELIVER_INTENT permits the same beahviour as START_STICKY but when the service is restarted, the last intent instead of null is given to onStartCommand
- With the constant START_NOT_STICKY the service is not restarted after being destroyed by the system
Foreground service
- Service are usually used in a foreground mode (using startForegroundService)
- A service that is not promoted to a foreground service within the first seconds of its existence is killed by the modern versions of the Android system
- Thus a service that is not in the foreground can only execute quick tasks (even if it use a secondary thread, it can be killed by the system)
- To promote a service to the foreground, we use the startForeground(int id, Notification notification) method (the identifier must not be zero)
-
A foreground service must show a notification that is persistent in the notification drawer: this way the user is always aware of the execution of the service
- The complete application (not only the service) can be stopped directly from the notification drawer since Android 13
- Since a foreground service is permanently executed, it could drain battery
Use cases for a foreground service:
- A service that permanentely log the location of the user to a database
- A messaging service that is permanently connected to a server with a websocket
- A music player service using the MediaPlayer
- ...
To use a foreground service, a (non sensitive) permission must be declared in the manifest:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ...>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/>
<application ...>
...
</application>
</manifest>
Privacy restrictions for the services (since Android 11)
A service that uses the location API, the camera and/or the microphone must be declared as such in the manifest (and the app must own the appropriate permissions):
<manifest>
...
<service ...
android:foregroundServiceType="location|camera|microphone" />
</manifest>
When a foregound service is started when no activity of the app is visible:
- If the service uses the location API it must have the ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION permission (in addition to the ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION and ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)
- The service cannot access the microphone and the camera (thus it is impossible for an non privilegied app to start a service that spies the microphone when the device starts; an action of the user is required)
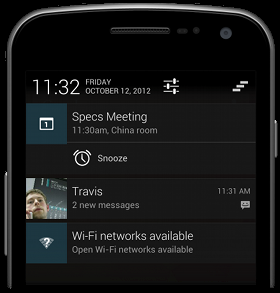
About notifications
- A service can display zero, one or several notifications simultaneously (a foreground service must display at least one notification to show its presence)
- Notifications appear in the notification drawer that is customized by the user
-
Graphical feedback for a notification:
- small icon in the top notification bar
- collapsed view in the open drawer
- extended view in the open drawer
-
full screen notification starting an activity (with setFullScreenIntent() and the permission USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT)
- to be used only for the most important notifications since it is very intrusive
How to create or update a notification?
- A notification channel must be created
- A notification must be build using NotificationCompat.Builder.build()
- An instance of the notification manager must be obtained with Context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE)
- The notification must be submitted to the notification manager with nm.notify(String tag, int id, Notification notification)
- The notification can be updated by calling again the notify method with a new updated notification and the same id
- One can also use startForeground(int id, Notification notification) to set the notification for a foreground service
- It is possible to use several notification channels to submit several notification; each channel can be configured independentely in the system settings (to silence it for example)

Since Android 13 (API level 33), the POST_NOTIFICATIONS permission must be declared in the manifest to create notifications. It is a dangerous permission: the app must ask explicitely the authorization. For apps targeting API levels < 33, a dialog to ask the permission is automatically launched when the notification channel is created.
Example: a notifying chronometer
Example of a service displaying a chronometer with a notification of the elapsed time (the highPriority mode displays the notification in heads-up mode without having to unwrap the notification drawer).
public class ChronoService extends Service
{
public static final String ACTION_START =
NotifiedChronometer.class.getPackage().getName() + ".startChronometer";
public static final String ACTION_STOP =
NotifiedChronometer.class.getPackage().getName() + ".startChronometer";
public static final String ACTION_RESET =
NotifiedChronometer.class.getPackage().getName() + ".resetChronometer";
// We don't use the RPC capability
@Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return null; }
private ChronoService instance = null;
private long cumulatedTime = 0;
private long startTime = -1;
private static boolean running = false;
private Thread updateThread = null;
/** Return if the chronometer is running */
public static boolean isRunning()
{
return running;
}
/** Identifier of the channel used for notification (required since API 26) */
public static final String CHANNEL_ID =
ChronoService.class.getName() + ".CHRONO_CHANNEL";
/** This method creates a new notification channel (required for API 26+)
* It is copied from https://developer.android.com/training/notify-user/build-notification
*/
private void createNotificationChannel()
{
// Create the NotificationChannel, but only on API 26+ because
// the NotificationChannel class is new and not in the support library
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
CharSequence name = "Chronometer channel";
String description = "Channel for notifications of the chronometer service";
int importance = NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT;
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(CHANNEL_ID, name, importance);
channel.setDescription(description);
// Register the channel with the system; you can't change the importance
// or other notification behaviors after this
NotificationManager notificationManager = getSystemService(NotificationManager.class);
notificationManager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
}
}
private Notification createNotification(String text, boolean highPriority)
{
NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder =
new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, CHANNEL_ID)
.setSmallIcon(android.R.drawable.ic_media_play)
.setContentTitle("Chronometer")
.setContentText(text)
.setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_DEFAULT)
.setSilent(true);
// if high priority is set, the notification is displayed in a heads-up fashion
if (highPriority) {
mBuilder.setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_HIGH);
mBuilder.setDefaults(Notification.DEFAULT_VIBRATE);
}
// Associate an action to the notification to start a linked Activity
Intent resultIntent = new Intent(this, NotifiedChronometer.class)
.putExtra("running", startTime >= 0);
// do not start the activity again if it is already on top
resultIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP);
mBuilder.setContentIntent(PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, resultIntent, 0));
return mBuilder.build();
}
@Override
public void onCreate()
{
super.onCreate();
instance = this; // set the singleton instance
createNotificationChannel();
}
/** Arbitrary ID for the notification (with different IDs a service can manage several notifications) */
public static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 1;
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId)
{
final NotificationManager nm = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
if (intent == null) return Service.START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY;
if (intent.getAction().equals(ACTION_START) && startTime == -1)
{
Log.i(getClass().getName(), "Action started intercepted");
final boolean highPriority = intent.getBooleanExtra("highPriority", false);
startTime = System.nanoTime();
// Put in the foreground
running = true;
startForeground(NOTIFICATION_ID, createNotification("Running chrono", highPriority));
// we could post update runnables on an handler instead of using a thread
updateThread = new Thread(() -> {
while (! Thread.interrupted())
{
long time = (cumulatedTime + System.nanoTime() - startTime) / 1000000000;
nm.notify(NOTIFICATION_ID, createNotification("Running: " + time + " s", highPriority));
System.err.println("Notify " + time);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
return; // the thread was interrupted (if the service is destroyed for example)
}
}
});
updateThread.start();
}
else if (intent.getAction().equals(ACTION_STOP) && startTime >= 0)
{
cumulatedTime += System.nanoTime() - startTime;
stopForeground(true);
running = false;
// remove the notification and stop the thread
nm.cancel(NOTIFICATION_ID);
updateThread.interrupt();
startTime = -1;
// stopSelf();
}
else if (intent.getAction().equals(ACTION_RESET))
{
if (startTime >= 0) startTime = System.nanoTime();
cumulatedTime = 0;
}
return START_NOT_STICKY; // do not restart automatically the service if it is killed
// however with startForeground, probability of service killing is weak
}
@Override
public void onDestroy()
{
// do not forget to stop the thread if the service is destroyed
if (updateThread != null) updateThread.interrupt();
}
}
Starting a service for the first time
- A service cannot start by itself: an action must be priorly done to run it.
- The user must start for a first time an activity of the application; the activity can execute a startService to launch the service
- If the user does not interact with an activity of the application during a long time, the application can be put in an hibernated mode and the service can be disabled
Starting a service at boot
- A service can be started at boot by using a BroadcastReceiver filtering the BOOT_COMPLETED action
- There is a variant broadcast (available from API level 24) named ACTION_LOCKED_BOOT_COMPLETED that is sent earlier when the device is booted before the first unlock by the user (BOOT_COMPLETED is sent after the first unlock)
- When the boot broadcast is sent, the BroadcastReceiver declared in the manifest is instantied and executed: the onReceive method can start the service with startService
- To receive the BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast, one must declare the permission in the manifest (it is not a sensitive permission: the declaration is enough to use it without needing to ask the user)
Declaration of the permission and the broadcast receiver in the manifest:
<manifest ...>
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
...
<application ...>
...
<receiver
android:name=".receivertest.BootBroadcastReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
...
</application>
</manifest>
Starting the service from the receiver:
class BootBroadcastReceiver : BroadcastReceiver() {
override fun onReceive(context: Context, intent: Intent) {
// This method is called when the BroadcastReceiver is receiving an Intent broadcast.
context.startService(Intent(context, ToastService::class.java).apply {
action = ToastService.TOAST_ACTION
putExtra("message", "Toast at boot!")
})
}
}
Communicating with a service
- We can submit asynchronously tasks to the service with intents using the startService call
- But it is more difficult for a service to communicate with its caller
- First way: by exposing synchronous remote methods (but it is not straighforward)
- Second way: by sending broadcast with a customized action (and listening for this kind of broadcast)
Example: a location logger service
- This service logs in a file the location of the user.
-
It requires the following permissions:
- ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION and ACCESS_FILE_LOCATION to obtain the location (the permission must be asked with a dialog to the user)
- ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION to use the location API in a service
- The service is declared in the manifest:
<service android:name=".gpslogger.LocationLoggerService"
android:foregroundServiceType="location" />
We write the service that logs the location and emits a broadcast with the location:
/** A simple service that logs locations into a file.
* It must be activated by a companion activity that must check that the location permissions are enabled.
*
* @author chilowi at u-pem.fr
*/
public class LocationLoggerService extends Service
{
public static final String LOCATION_FILE = "locations.log";
public static final String LOCATION_BROADCAST_ACTION = LocationLoggerService.class.getName() + ".LOCATION_INFO";
LocationManager locationManager = null;
LocationListener locationListener = null;
Writer writer = null;
private static boolean running = false;
public static boolean isRunning()
{
return running;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) { return null; }
public static final String CHANNEL_ID = "locationLogger";
/** This method creates a new notification channel (required for API 26+)
* It is copied from https://developer.android.com/training/notify-user/build-notification
*/
private void createNotificationChannel()
{
// Create the NotificationChannel, but only on API 26+ because
// the NotificationChannel class is new and not in the support library
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
CharSequence name = "Location logger channel";
String description = "Channel for the location logger";
int importance = NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT;
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel(CHANNEL_ID, name, importance);
channel.setDescription(description);
// Register the channel with the system; you can't change the importance
// or other notification behaviors after this
NotificationManager notificationManager = getSystemService(NotificationManager.class);
notificationManager.createNotificationChannel(channel);
}
}
private Notification createNotification()
{
NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder =
new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, CHANNEL_ID)
.setSmallIcon(android.R.drawable.ic_media_play)
.setContentTitle("Location logger")
.setContentText("The logger is active")
.setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_DEFAULT)
.setSilent(true);
return mBuilder.build();
}
private void log(String message)
{
try {
if (writer == null)
{
writer = new OutputStreamWriter(openFileOutput(LOCATION_FILE, MODE_APPEND));
}
writer.write(new Date() + ": " + message);
writer.flush();
} catch (IOException e)
{
Log.e(getClass().getName(), "Cannot log message " + message + " due to an exception", e);
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate()
{
createNotificationChannel();
locationManager = (LocationManager)getSystemService(LOCATION_SERVICE);
locationListener = new LocationListener() {
@Override public void onStatusChanged(String provider, int status, Bundle extras)
{
log(String.format("Change of status of provider %s: %d", provider, status));
}
@Override public void onProviderEnabled(String provider)
{
log(String.format("Provider %s is enabled", provider));
}
@Override public void onProviderDisabled(String provider)
{
log(String.format("Provider %s is disabled", provider));
}
@Override public void onLocationChanged(Location location)
{
log(String.format("latitude=%f, longitude=%f, altitude=%f",
location.getLatitude(), location.getLongitude(), location.getAltitude()));
Intent i = new Intent(LOCATION_BROADCAST_ACTION);
i.putExtra("latitude", location.getLatitude());
i.putExtra("longitude", location.getLongitude());
sendBroadcast(i);
}
};
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId)
{
startForeground(1, createNotification());
try {
String provider = intent.getStringExtra("provider");
if (provider == null) provider = LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER;
locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(provider,
intent.getLongExtra("minTime", 10000),
intent.getFloatExtra("minDistance", 100.0f),
locationListener);
running = true;
} catch (SecurityException e)
{
Toast.makeText(this, "Cannot start the location logger service", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
stopSelf();
}
return Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT; // Restart the service with the intent if it is destroyed
}
@Override
public void onDestroy()
{
try { if (writer != null) writer.close(); } catch (IOException ignored) {}
try {
locationManager.removeUpdates(locationListener);
} catch (SecurityException e)
{
// this case should not be encountered
}
running = false;
}
}
And we write the activity that starts the service and listen for the broadcasted locations with a receiver:
class LocationLoggerActivity : RequiringPermissionActivity() {
var serviceIntent: Intent? = null
var receiver = object: BroadcastReceiver() {
override fun onReceive(context: Context, intent: Intent) {
val infoTextView = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.infoTextView)
val latitude = intent.getDoubleExtra("latitude", Double.NaN)
val longitude = intent.getDoubleExtra("longitude", Double.NaN)
infoTextView.text = "Update received on ${Date()}: $latitude/$longitude"
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
serviceIntent = Intent(this, LocationLoggerService::class.java)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_location_logger)
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val cb = findViewById<CheckBox>(R.id.locationLoggerServiceCheckBox)
runWithPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, "You must grant the GPS permission",
{Toast.makeText(this, "Location permission is not granted", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
cb.isEnabled = false},
{cb.isEnabled = true})
cb.isChecked = LocationLoggerService.isRunning()
registerReceiver(receiver, IntentFilter(LocationLoggerService.LOCATION_BROADCAST_ACTION))
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
unregisterReceiver(receiver)
}
fun onCheckBoxClick(v: View) {
val action = if ((v as CheckBox).isChecked) { x: Intent? -> startService(x) } else { x -> stopService(x) }
action(serviceIntent)
}
}
WorkManager
Principles
- WorkManager is a high level API to schedule tasks that do not require immediate graphical feedback
-
Relies on the low level APIs:
- AlarmManager + BroadcastReceiver (if API level ∈ [14,22])
- JobScheduler (if API level ≥ 23)
How to create a work that can be submitted?
- We write a class that inherits from Worker that overrides the Result doWork() to do the task
- We create a WorkRequest with the worker and the execution constraints (battery level, charging mode, CPU level...); one use WorkRequest.Builder to build the request
- We submit the WorkRequest to the WorkManager that places it in the queue
- We can register an observer to receives WorkInfo to be informed about the status of the task (pending, running or finished)
-
We can cancel a task with the WorkManager that is pending or running
- The task must cooperate and check itself in the doWork() method if it is cancelled with isStopped()
- We can build complex tasks by pipelining output from tasks to other tasks
Example of a submitted task
We want to retrieve periodically (every 15 minutes) the conversion rates of an API in the background.
We write the Worker (using a Listenable<Worker>) to do the retrieval task (a cache file is stored with the result) :
/** Worker that retrieves currency rates */
class CurrencyFetchingWorker(context: Context, params: WorkerParameters): ListenableWorker(context, params) {
companion object {
const val REQUEST_URL = "https://api.ratesapi.io/api/latest"
const val RATES_FILENAME = "currencyRates.json"
}
override fun startWork(): ListenableFuture<Result> {
return CallbackToFutureAdapter.getFuture { completer ->
val stringRequest = StringRequest(Request.Method.GET, REQUEST_URL,
{ response -> // write the result to the RATES file
applicationContext.cacheDir.resolve(RATES_FILENAME).writeText(response)
},
object : Response.ErrorListener {
override fun onErrorResponse(error: VolleyError) {
Toast.makeText(applicationContext, "Cannot fetch rates due to " + error, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
Log.e(this.javaClass.name, "Error while retrieving rates", error)
completer.set(Result.failure())
}
}
)
//Instantiate the RequestQueue and add the request to the queue
val queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(applicationContext)
queue.add(stringRequest)
"currencyJob"
}
}
}
We write an activity to start or stop the retrieving tasks:
class CurrencyActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
companion object {
const val JOB_NAME = "fetchingCurrencyRates"
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_currency)
WorkManager.getInstance(this).apply {
val data = getWorkInfosForUniqueWorkLiveData(JOB_NAME)
// create an observer to be informed about the status of the job
val observer = Observer { list: List<WorkInfo> ->
currencyJobStatus.text = if (list.isNotEmpty()) list[0].state.toString() else "unknown status"
currencyRatesTextView.text = try {
val f = cacheDir.resolve(CurrencyFetchingWorker.RATES_FILENAME)
"Modification date: ${Date(f.lastModified())}\n\n${f.readText()}"
} catch (e: IOException) {
"data not available yet"
}
}
data.observe(this@CurrencyActivity, observer)
}
}
fun startJob(v: View) {
val constraints = Constraints.Builder()
.setRequiredNetworkType(NetworkType.CONNECTED)
.setRequiresBatteryNotLow(true)
.build()
// ask to fetch the currency rates every 15 minutes if network is available and battery not low
val request = PeriodicWorkRequestBuilder<CurrencyFetchingWorker>(15L, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.setConstraints(constraints)
.setBackoffCriteria(BackoffPolicy.LINEAR, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.addTag(JOB_NAME)
.build()
WorkManager.getInstance(this).apply {
enqueueUniquePeriodicWork(JOB_NAME, ExistingPeriodicWorkPolicy.REPLACE, request)
}
}
fun stopJob(v: View) {
WorkManager.getInstance(this).apply {
cancelUniqueWork(JOB_NAME)
}
}
}
Priority Buckets
The applications are put in 5 priority buckets according to their usage:
- Active: the application is running an activity in the foreground or have been recently used
- Working set: the application is regularly used
- Frequent: the application is used but not daily
- Rare: the application is rarely used
- Restricted : the application is restricted due to an abuse of resources
- It is possible to know the current bucket of the application with UsageStatsManager
- The bucket of an app can be changed by hand with adb shell am set-standby-bucket PACKAGE_NAME restricted (for example to put the app in the restricted bucket and test its behaviour in this case)